Combating Plastic Pollution: Strategies for a Sustainable Future
Introduction
Plastic pollution has become a global crisis, posing significant threats to our environment, wildlife, and human health. With the exponential growth in plastic production and consumption over the past few decades, our planet is drowning in plastic waste. It’s imperative that we take swift and decisive action to address this issue before irreversible damage is done. In this article, we’ll explore the causes and consequences of plastic pollution and discuss effective strategies for mitigating its impact.
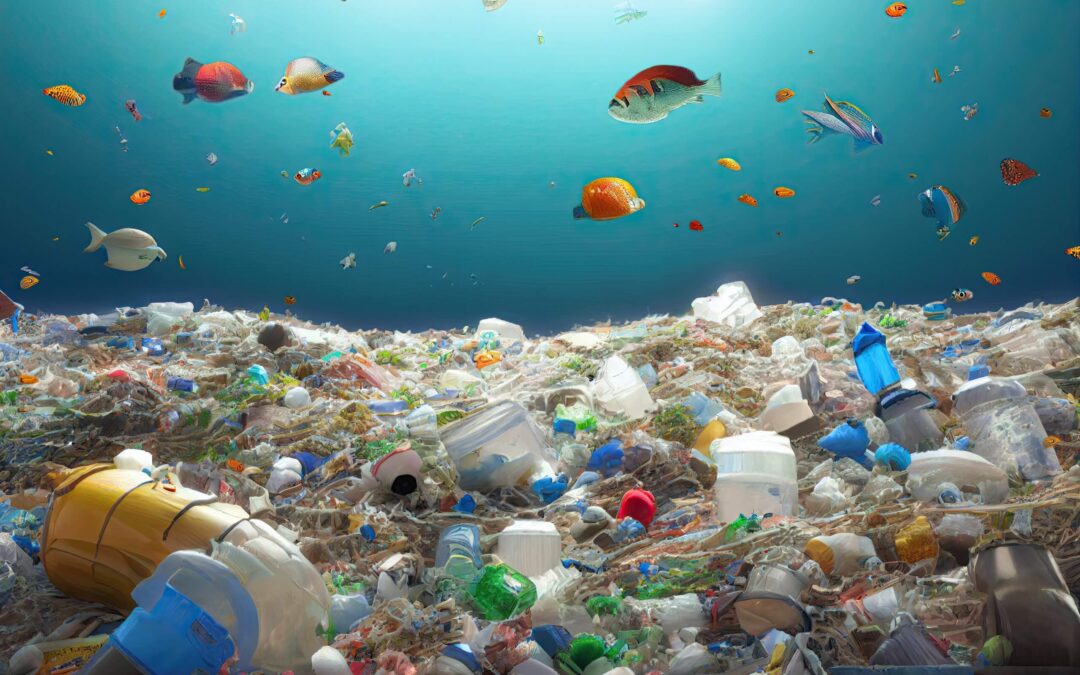
The Scope of the Problem: Plastic pollution encompasses a wide range of environmental issues, from littered beaches and waterways to microplastics contaminating our soil and oceans. Every year, millions of tons of plastic waste enter our environment, with devastating effects on marine life, ecosystems, and human health. Marine animals often mistake plastic debris for food, leading to ingestion and entanglement, which can be fatal. Furthermore, microplastics have been found in drinking water, seafood, and even the air we breathe, raising concerns about their potential health risks.
Causes of Plastic Pollution
The proliferation of plastic pollution can be attributed to various factors, including:
- Single-Use Plastics: Products like plastic bags, bottles, and packaging are designed for short-term use but persist in the environment for centuries, contributing significantly to pollution.
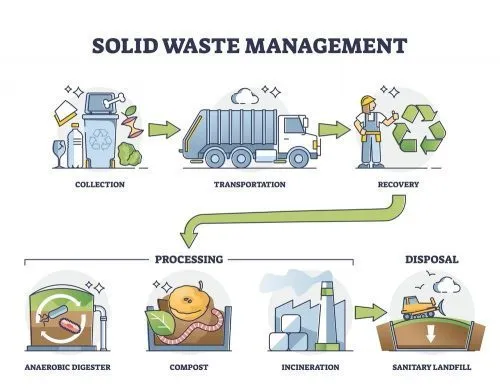
- Inadequate Waste Management: Insufficient recycling infrastructure and improper disposal practices lead to plastic waste accumulating in landfills, rivers, and oceans.
- Industrial Production: The mass production of plastic products, fueled by the petrochemical industry, exacerbates the problem by generating vast amounts of non-biodegradable waste.
- Consumer Behavior: Our throwaway culture and reliance on convenience contribute to the overconsumption and disposal of plastic items.
Strategies for Mitigation: Addressing plastic pollution requires a multi-faceted approach involving governments, industries, communities, and individuals. Here are some key strategies to combat plastic pollution:
- Policy Interventions: Governments must implement regulations to reduce plastic production, ban single-use plastics, and promote sustainable alternatives. Extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes can hold manufacturers accountable for the lifecycle of their products.
- Innovation and Technology: Investing in research and development of eco-friendly materials and recycling technologies can facilitate the transition to a circular economy where plastics are reused, recycled, or composted.
- Public Awareness and Education: Raising awareness about the environmental impacts of plastic pollution and encouraging behavior change through education campaigns can foster a culture of sustainability.
- Corporate Responsibility: Businesses should adopt environmentally responsible practices, such as using recycled materials, redesigning packaging for recyclability, and reducing plastic usage in their operations.
- Community Engagement: Local initiatives, such as beach clean-ups, plastic-free campaigns, and community recycling programs, empower citizens to take action at the grassroots level.
Conclusion
Plastic pollution is a complex and pervasive problem that demands urgent attention and collective action. By implementing a combination of policy measures, technological innovations, public awareness campaigns, and corporate initiatives, we can work towards a future where plastic pollution is minimized, and our planet is healthier and more sustainable for generations to come. Let us commit to preserving our environment and protecting the precious ecosystems that sustain life on Earth.